PhaSeDis: A manually curated database of the relations between phase separation and diseases
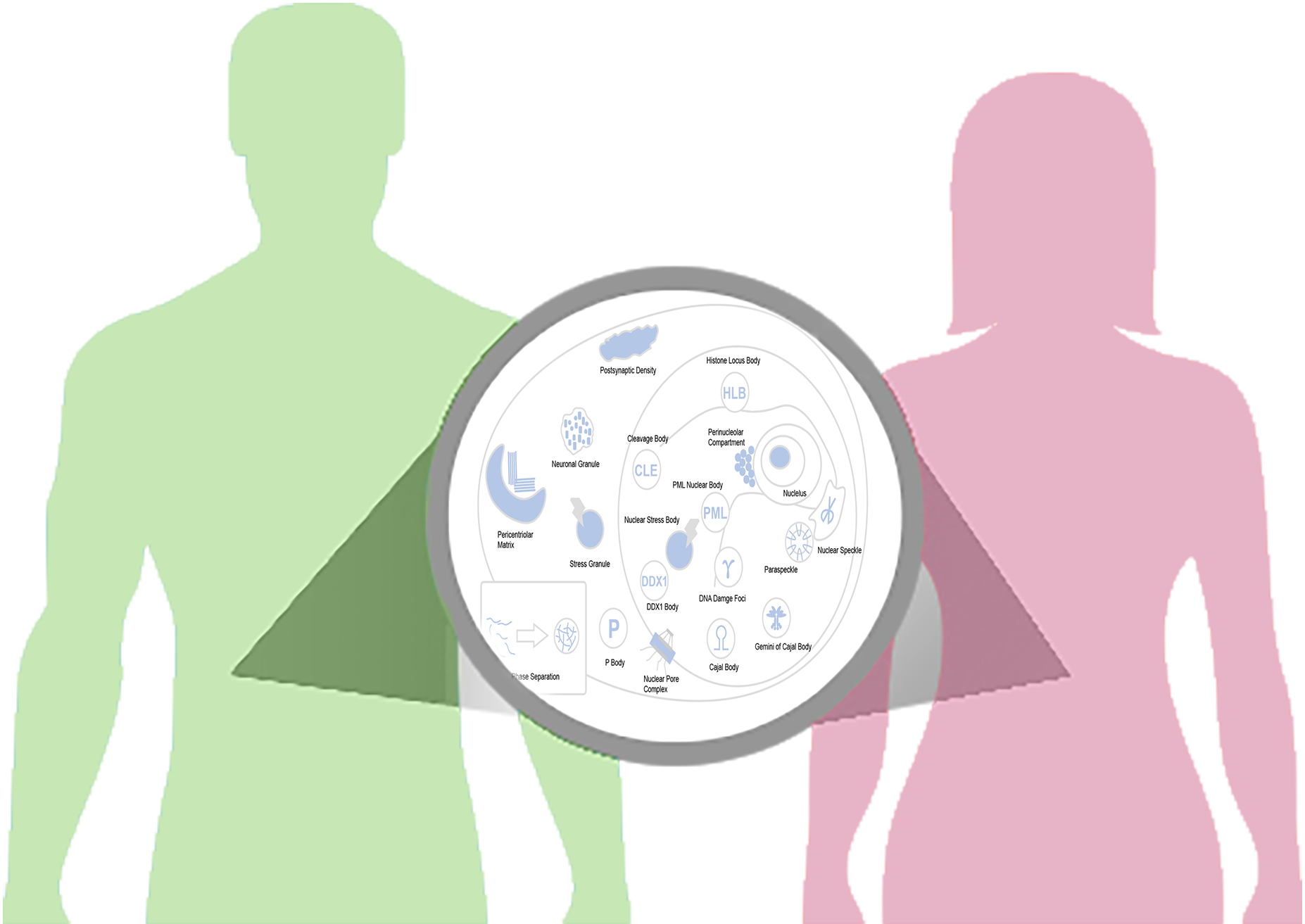
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) plays an important role in the temporal and spatial regulation of various biological processes, and emerging evidence supports that LLPS might serve as the underlying mechanism of membraneless organelle (MLO)
assembly. Dysfunction of LLPS and MLOs are associated with various pathological processes. PhaSeDis aims to gather LLPS and MLOs related diseases from the dispersed literature. Each entry was assigned with one of the three evidence levels based on
original publication: Direct experiment, Indirect experiment, Clinical Investigation. PhaSeDis not only recorded the functional factors, changes of MLOs/LLPS droplets and changes of the factors according to the original publication, but also includes
the components of MLOs and small molecules that target the LLPS factors with low-throughput and high-throughput evidences
(go to About for detail).
Examples: Stress Granule, FUS, Parkinson's disease
Browse
Browse all entries in PhaSeDis by combinatorial search. For example, you can specify the MLO name and the disease.
MLOs
Explore PhaSeDis by MLOs, you can see the description, related diseases and components of the MLO.
Diseases
Explore PhaSeDis by diseases, you can see all the diseases included in our database and search by human body systems.
News
2023-06-15: MloDisDB has been updated into PhaSeDis.
2020-09-19: Accepted by Briefings in Bioinformatics.https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa271
2020-09-14: Each entry was assigned with one of the three evidence levels based on original publication: Direct experiment, Indirect experiment, Clinical Investigation.
2020-06-18: MloDisDB 1.0 is online, 719 relations between MLOs and diseases, 52 relations between LLPS and diseases were included.
Chao Hou, Haotai Xie, Yang Fu, Yao Ma, Tingting Li. MloDisDB: A manually curated DataBase of the relations between MembraneLess Organelles and DISeases